Gnomad database citation information
Home » Trend » Gnomad database citation informationYour Gnomad database citation images are ready. Gnomad database citation are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Gnomad database citation files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for gnomad database citation images information related to the gnomad database citation keyword, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with suggestions for seeing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
Gnomad Database Citation. The two points that seem to finally be getting real attention by the community (but still not quite there) are Robert castelo <robert.castelo at upf.edu>. There is much more data to come: Here, we describe the aggregation of 125,748 exomes and 15,708 genomes from human sequencing studies into the genome aggregation database (gnomad).
 Polymorphism leading to truncated human ZP4 protein can be From researchgate.net
Polymorphism leading to truncated human ZP4 protein can be From researchgate.net
The team has not been idle since the release of the gnomad v2 dataset. One thought on “ annotating with gnomad: Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad release 2.1) for the human genome version grch38. Here, we describe the aggregation of 125,748 exomes and 15,708 genomes from human sequencing studies into the genome aggregation database (gnomad). Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad version 3.1.1) for the human genome version grch38. The gnomad database is a useful, publicly available collection of human sequence data, but there are a number of caveats that are important to note when drawing inf erences about variant
Citation (from within r, enter citation (mafdb.gnomad.r2.1.grch38) ):
There is much more data to come: Here we present a pipeline to call mtdna variants that addresses three technical challenges: Here, we describe the aggregation of 125,748 exomes and 15,708 genomes from human sequencing studies into the genome aggregation database (gnomad). The gnomad database is a useful, publicly available collection of human sequence data, but there are a number of caveats that are important to note when drawing inf erences about variant In its first release, which contained exclusively exome data, it was known as the. To curate the grch38 version of this annotation there was an extra liftover step.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
To curate the grch38 version of this annotation there was an extra liftover step. In its first release, which contained exclusively exome data, it was known as the. Frequencies from 123,136 exomes and 15,496 genomes ” larry babb may 18, 2017 at 7:31 am. The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data. There is much more data to come:

Mv frequency within the genome aggregation database (gnomad) (n = 141,352 individuals) was assessed, and mvs were analyzed with 8 in silico tools. 10.18129/b9.bioc.mafh5.gnomad.v3.1.1.grch38 minor allele frequency data from gnomad version 3.1.1 for grch38. Here we present a pipeline to call mtdna variants that addresses three technical challenges: This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. There is much more data to come:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Robert castelo <robert.castelo at upf.edu>. This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data. In its first release, which contained exclusively exome data, it was known as the. Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad release 2.1) for the human genome version grch38.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data. The development team at golden helix has curated this database for both grch37 and grch38. Mv frequency within the genome aggregation database (gnomad) (n = 141,352 individuals) was assessed, and mvs were analyzed with 8 in silico tools. This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. Here we present a pipeline to call mtdna variants that addresses three technical challenges:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In its first release, which contained exclusively exome data, it was known as the. Citation (from within r, enter citation (mafdb.gnomad.r2.1.grch38) ): The team has not been idle since the release of the gnomad v2 dataset. The two points that seem to finally be getting real attention by the community (but still not quite there) are Databases of allele frequency are extremely helpful for evaluating clinical variants of unknown significance;
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Citation (from within r, enter citation (mafdb.gnomad.r2.1.grch38) ): The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data. Databases of allele frequency are extremely helpful for evaluating clinical variants of unknown significance; In the present work, we report a detailed population and bioinformatic prediction analyses of the tg variants indexed in the genome aggregation database (gnomad). There is much more data to come:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad version 3.1.1) for the human genome version grch38. Here, we describe the aggregation of 125,748 exomes and 15,708 genomes from human sequencing studies into the genome aggregation database (gnomad). In the present work, we report a detailed population and bioinformatic prediction analyses of the tg variants indexed in the genome aggregation database (gnomad). There is much more data to come: The gnomad database is a useful, publicly available collection of human sequence data, but there are a number of caveats that are important to note when drawing inf erences about variant
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Mv frequency within the genome aggregation database (gnomad) (n = 141,352 individuals) was assessed, and mvs were analyzed with 8 in silico tools. However, until now, genetic databases such as the genome aggregation database (gnomad) have ignored the mitochondrial genome (mtdna). Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad version 3.1.1) for the human genome version grch38. Databases of allele frequency are extremely helpful for evaluating clinical variants of unknown significance; 10.18129/b9.bioc.mafh5.gnomad.v3.1.1.grch38 minor allele frequency data from gnomad version 3.1.1 for grch38.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
One thought on “ annotating with gnomad: This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. To curate the grch38 version of this annotation there was an extra liftover step. There is much more data to come: The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data.
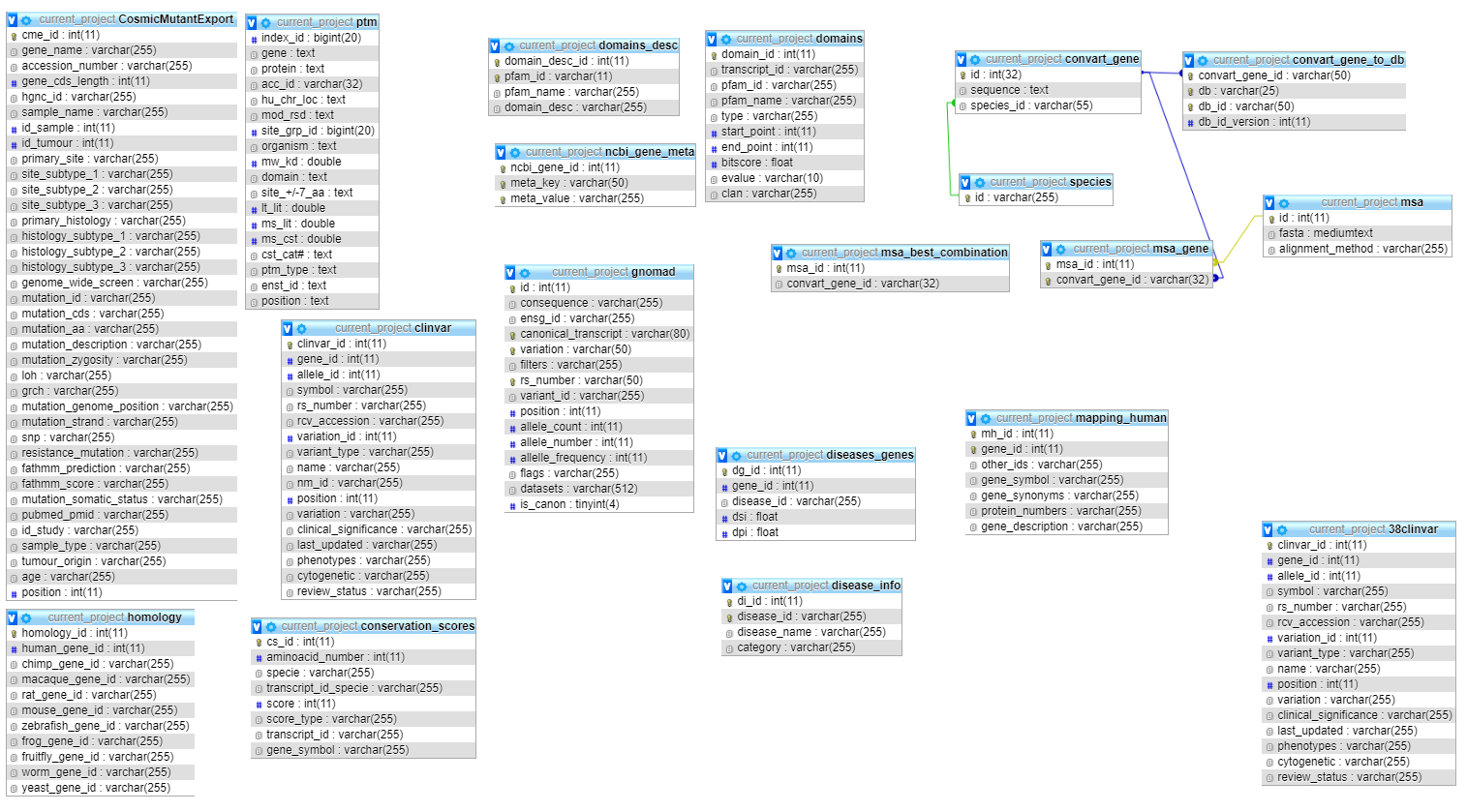 Source: convart.org
Source: convart.org
Most of the sequence data in gnomad is. One thought on “ annotating with gnomad: Robert castelo <robert.castelo at upf.edu>. 10.18129/b9.bioc.mafh5.gnomad.v3.1.1.grch38 minor allele frequency data from gnomad version 3.1.1 for grch38. Citation (from within r, enter citation (mafdb.gnomad.r2.1.grch38) ):
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad release 2.1) for the human genome version grch38. To curate the grch38 version of this annotation there was an extra liftover step. The development team at golden helix has curated this database for both grch37 and grch38. This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. Here we present a pipeline to call mtdna variants that addresses three technical challenges:
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Mv frequency within the genome aggregation database (gnomad) (n = 141,352 individuals) was assessed, and mvs were analyzed with 8 in silico tools. Citation (from within r, enter citation (mafdb.gnomad.r2.1.grch38) ): The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data. The gnomad database is a useful, publicly available collection of human sequence data, but there are a number of caveats that are important to note when drawing inf erences about variant In its first release, which contained exclusively exome data, it was known as the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Mv frequency within the genome aggregation database (gnomad) (n = 141,352 individuals) was assessed, and mvs were analyzed with 8 in silico tools. Mv frequency within the genome aggregation database (gnomad) (n = 141,352 individuals) was assessed, and mvs were analyzed with 8 in silico tools. This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. Most of the sequence data in gnomad is. To curate the grch38 version of this annotation there was an extra liftover step.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
There is much more data to come: The development team at golden helix has curated this database for both grch37 and grch38. 10.18129/b9.bioc.mafh5.gnomad.v3.1.1.grch38 minor allele frequency data from gnomad version 3.1.1 for grch38. Release (3.14) store minor allele frequency data from the genome aggregation database (gnomad release 2.1) for the human genome version grch38. The team has not been idle since the release of the gnomad v2 dataset.
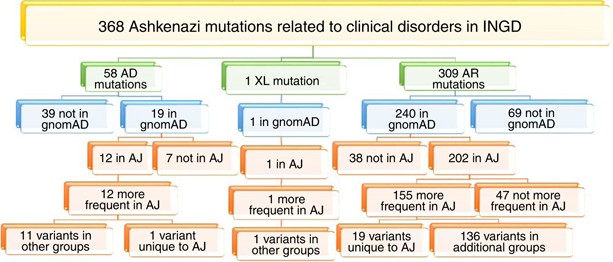 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The gnomad database is a useful, publicly available collection of human sequence data, but there are a number of caveats that are important to note when drawing inf erences about variant 10.18129/b9.bioc.mafh5.gnomad.v3.1.1.grch38 minor allele frequency data from gnomad version 3.1.1 for grch38. To curate the grch38 version of this annotation there was an extra liftover step. Databases of allele frequency are extremely helpful for evaluating clinical variants of unknown significance; The team has not been idle since the release of the gnomad v2 dataset.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In a coordinated set of seven publications, the genome aggregation database ( gnomad) consortium presents a catalogue of human genetic. This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. In a coordinated set of seven publications, the genome aggregation database ( gnomad) consortium presents a catalogue of human genetic. The team has not been idle since the release of the gnomad v2 dataset. Most of the sequence data in gnomad is.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Robert castelo <robert.castelo at upf.edu>. Databases of allele frequency are extremely helpful for evaluating clinical variants of unknown significance; This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad. Most of the sequence data in gnomad is. Robert castelo <robert.castelo at upf.edu>.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The development team at golden helix has curated this database for both grch37 and grch38. The genome aggregation database (gnomad) is currently the largest and most widely used publicly available collection of population variation from harmonized sequencing data. In the present work, we report a detailed population and bioinformatic prediction analyses of the tg variants indexed in the genome aggregation database (gnomad). Here we present a pipeline to call mtdna variants that addresses three technical challenges: This review provides guidance on the content of the gnomad.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title gnomad database citation by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- De vliegeraar citaten information
- Full reference citation apa style information
- Free apa citation machine online information
- Etre amoureux citation information
- Fight club citation tyler information
- Evene lefigaro fr citations information
- Freud citations aimer et travailler information
- Endnote book citation information
- Flap lever cessna citation information
- Foreign aid debate citation information